Davos, Switzerland — January 19, 2026
The annual World Economic Forum (WEF) gathering in the Swiss Alps begins this Monday under the theme “A Spirit of Dialogue.” Leaders from governments, business, civil society and science will convene through January 23 to confront what organizers call the most pressing global challenges of our time: geopolitical instability, economic fragmentation, technological disruption and climate change.
This year’s meeting is poised to be one of the most unpredictable yet — largely because U.S. President Donald Trump is attending in person and will lead the largest-ever American delegation to Davos.
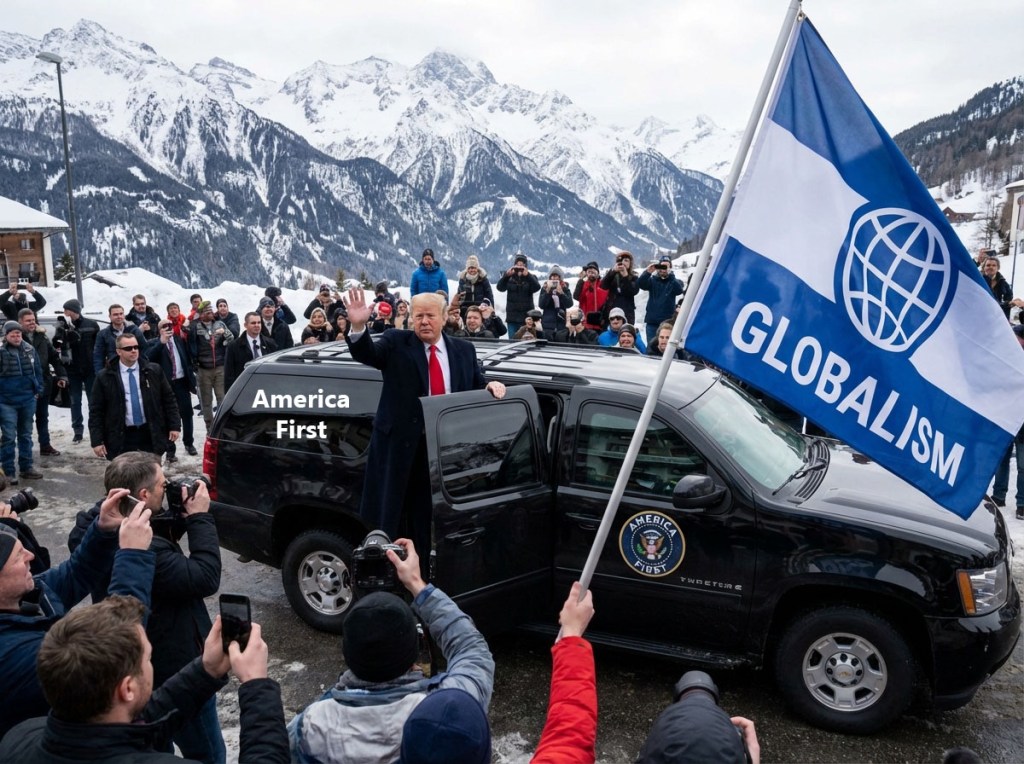

Trump Returns to Davos with a Big Team
Trump’s presence is notable not only for its scale but also for its political symbolism. His administration will be accompanied by several Cabinet members and senior officials — including the Secretary of State, Treasury Secretary, Commerce Secretary, trade representatives, and top White House aides — marking a record-size U.S. contingent.
Last time Trump engaged with the forum, his participation was virtual and aired amid controversy. This year’s in-person return is expected to attract rock-star style attention and intense scrutiny from global leaders, the media and activists.
A “Spirit of Dialogue” Amid Global Tensions
The forum’s theme emphasizes cooperation and conversation in a world marked by deepening geopolitical fault lines. Amid economic competition, rising tariffs and shifting alliances, WEF organizers are pushing dialogue as essential for progress.
But Trump’s trademark slogan, “America First,” poses a direct challenge to the forum’s ethos of multilateral cooperation. Allies and competitors alike will be watching to see how — and if — Trump’s policies can align with broader global ambitions for cooperation, especially on trade, security and technology.
Key Issues on the Agenda
While WEF is traditionally focused on economic strategy and global collaboration, this year’s agenda is exceptionally crowded:
- Geopolitical and security challenges: Ukraine remains a central topic, with talks planned involving U.S. officials and Ukrainian representatives about peace frameworks and reconstruction support.
- Economic fragmentation: A recent WEF risk survey found that economic confrontation — including tariffs and trade tensions — has overtaken armed conflict as a top risk to global stability.
- Artificial Intelligence: Discussions about how to govern and deploy AI responsibly are expected to be key, with tech leaders from companies such as Microsoft and Nvidia attending.
- Business and innovation: With roughly 3,000 participants and about 850 CEOs from top global companies, business and investment outlooks will be central to many discussions.
Trump’s Global Footprint Heading into Davos
Trump’s foreign policy moves over the past year — from threats of tariffs over Greenland to confrontations with Iran and Venezuela — have reshaped parts of the international agenda. European leaders are preparing for high-stakes talks with the U.S., including possible retaliatory measures tied to trade tensions that are already threatening transatlantic unity.
Although climate and “woke” cultural topics were reportedly de-emphasized in programming after negotiations with U.S. officials, the core business of the forum — economic cooperation and innovation — remains indispensable.
A Pivotal Moment for Global Order
This year’s Davos is widely perceived as a test of whether global leaders can adapt the old world order to 21st-century challenges — or whether a fundamentally new framework for cooperation will emerge. With Trump’s America firmly in the spotlight and AI and economic confrontation rising as cross-cutting issues, the balance between national interests and collective global action will be under intense scrutiny.
As the world’s eyes turn to the Swiss Alps, the question is no longer whether dialogue will take place — but whether it can translate into real solutions.

Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are those of the author and may not reflect those of Shinybull.com. The author has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information provided; however, neither Shinybull.com nor the author can guarantee the accuracy of this information. This article is strictly for informational purposes only. It is not a solicitation to make any exchange in precious metal products, commodities, securities, or other financial instruments. Shinybull.com and the author of this article do not accept culpability for losses and/ or damages arising from the use of this publication.