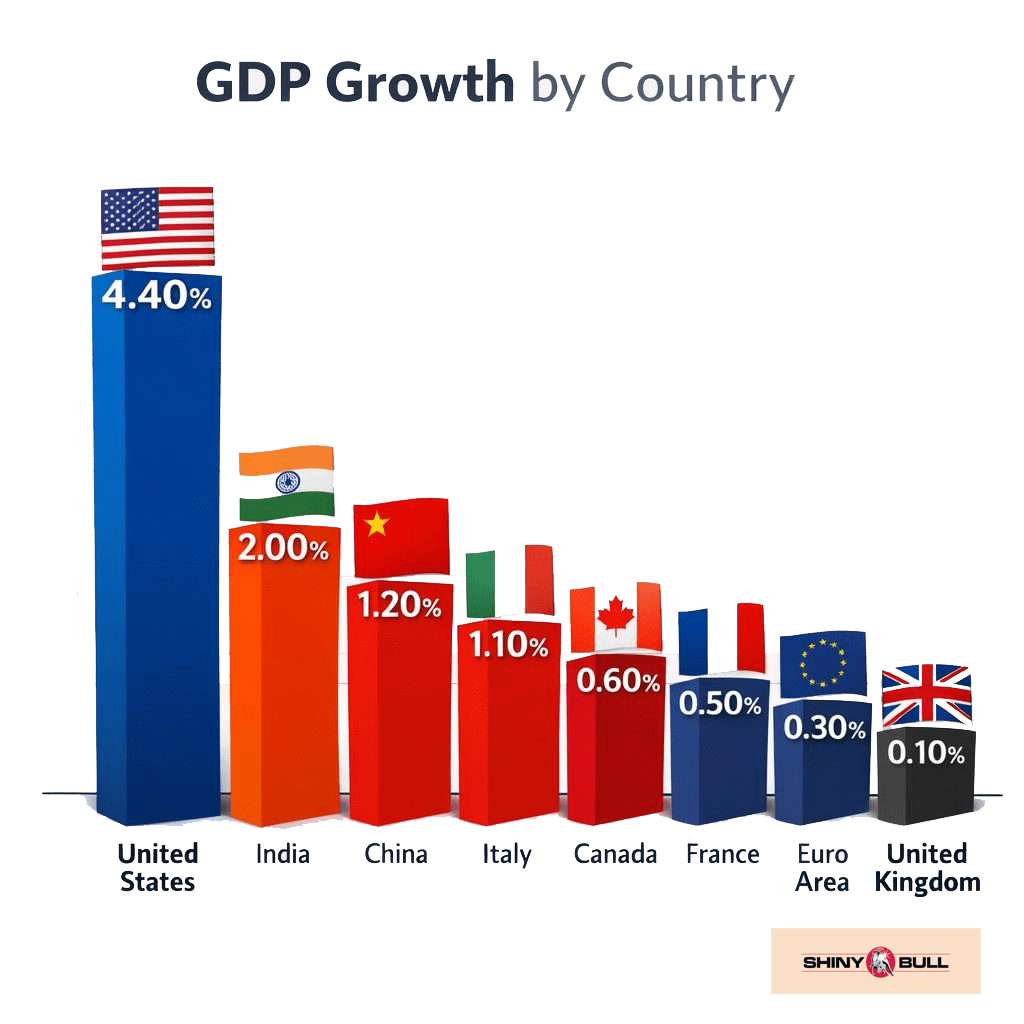
When we look at GDP growth, one thing becomes very clear: the United States is in a league of its own. With growth at 4.4 percent, the U.S. economy is running far ahead of other major economies.
India comes in second — but at less than half the U.S. rate. China, once the global engine of growth, is now barely above one percent. Europe paints a much weaker picture: the euro area, France, and the UK are hovering near stagnation. Italy does a bit better, but still far behind the U.S.
The takeaway is simple: global growth is no longer evenly distributed. The world is increasingly dependent on one dominant economic engine — the United States.
Trumponomics, Taxes, and Tariffs
This dominance is not accidental. Trumponomics — including tax cuts, deregulation, and strategic trade measures — has been designed to strengthen domestic growth. Lower taxes have incentivized investment, increased consumption, and created a multiplier effect across multiple sectors. Simply put: lower taxes mean more growth.
Tariffs have also contributed, protecting key industries and encouraging reshoring. While not the main driver of GDP growth, they amplify the effect of pro-growth policies, keeping production and capital inside the United States.
Crypto and Blockchain: America’s Catalyst
Digital infrastructure, crypto, and blockchain have emerged as powerful catalysts for U.S. economic dominance. While crypto-related activity still represents only a small fraction of U.S. GDP today, it facilitates faster capital flows, scalable services, and innovative financial systems.
Blockchain doesn’t drive the economy on its own — but it reinforces American economic advantage and positions the U.S. to maintain its lead as digital systems expand.
Blockchains are the future, not just for finance, but for the infrastructure of value itself. And America is at the forefront.
Innovation vs. Bureaucracy
A key driver behind continued U.S. economic growth is innovation—particularly in advanced manufacturing and energy technology. Companies like Tesla, led by Elon Musk, have played a pioneering role by pushing battery technology to a new level, giving the U.S. a clear competitive advantage in electric vehicles and energy storage.
In contrast, Europe—and Germany in particular—has been slowed by regulatory complexity and bureaucratic inertia. While innovation in the U.S. is often enabled by speed, scale, and risk-taking, European industry must navigate dense layers of regulation, approval processes, and political compromise.
For Germany, whose economy is deeply tied to the automotive sector, this loss of momentum has broader consequences. And as Germany remains the economic locomotive of the EU, the effects of slower innovation are amplified across Europe—raising the question of whether regulation has begun to outweigh competitiveness.
One Engine, Many Passengers
Put it all together: Trumponomics, smart policy, tariffs, and innovative digital infrastructure. The result? America continues to dominate while Europe struggles with stagnation, and China slows. Emerging markets chase momentum.
Growth today in the United States comes not from soil or oil alone, but from systems designed to turn value into profit. Lower taxes, strategic policy, and innovation create a self-reinforcing cycle — one that keeps the U.S. in the driver’s seat.
Oil once defined power. Today, code, capital, and blockchain define it. And in that world, the United States still owns the refinery.

Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are those of the author and may not reflect those of Shinybull.com. The author has made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information provided; however, neither Shinybull.com nor the author can guarantee the accuracy of this information. This article is strictly for informational purposes only. It is not a solicitation to make any exchange in precious metal products, commodities, securities, or other financial instruments. Shinybull.com and the author of this article do not accept culpability for losses and/ or damages arising from the use of this publication.








